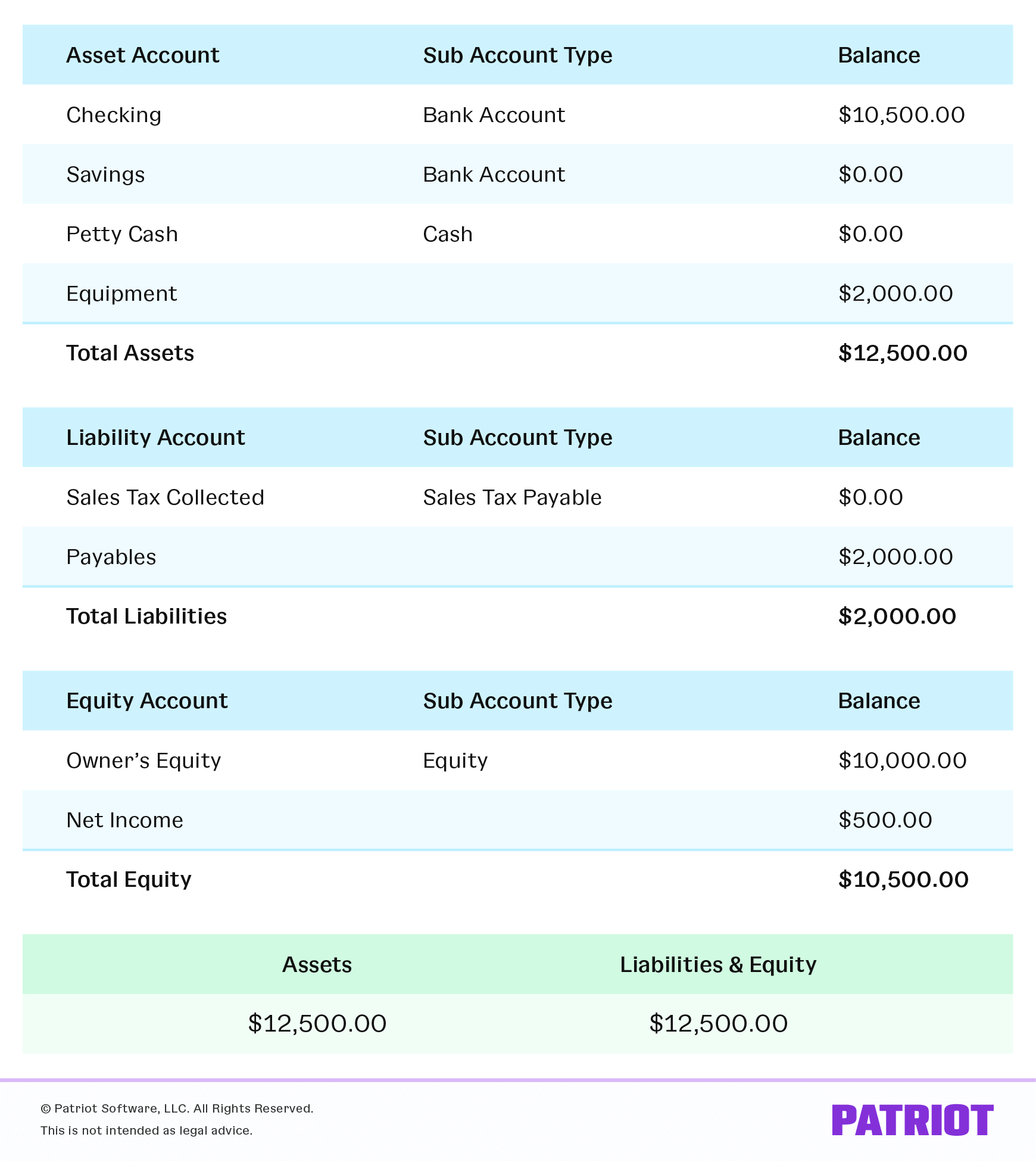
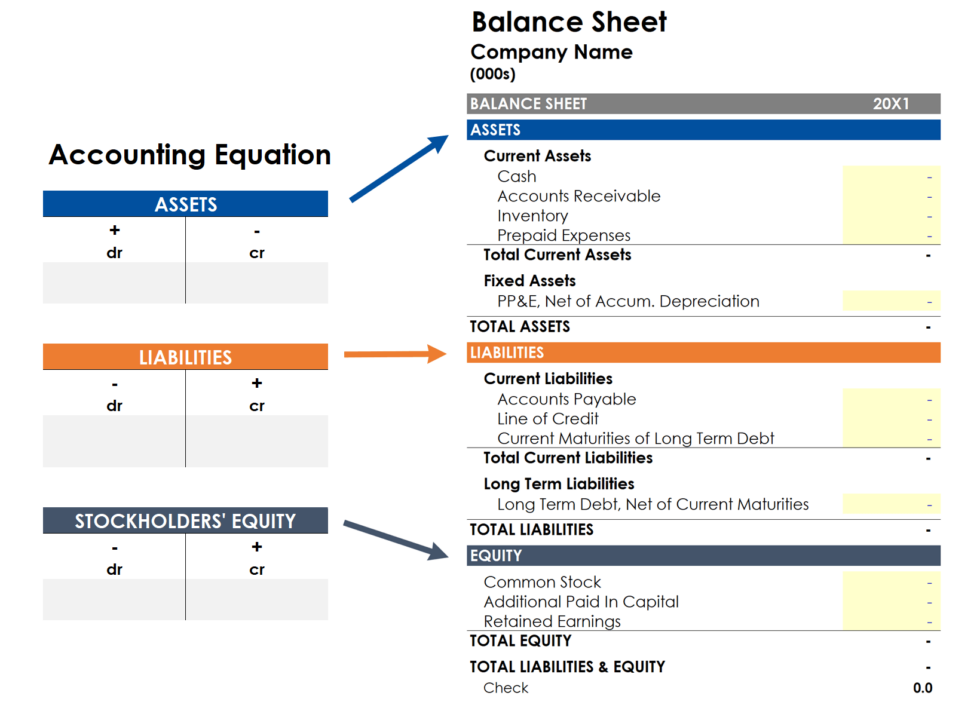
Balance Sheet Accounting Equation - The balance sheet is based on the fundamental equation: Assets = liabilities + equity. Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side. The formula reflects the fundamental accounting principle that the total value of a company's assets equals the sum of. The balance sheet formula is assets = liabilities + shareholders' equity. The structure of the balance sheet reflects the accounting equation: Assets = liabilities + stockholders’ (or owner’s) equity. As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides (or. The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle. The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance.
The structure of the balance sheet reflects the accounting equation: The balance sheet is based on the fundamental equation: Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side. Assets = liabilities + stockholders’ (or owner’s) equity. The formula reflects the fundamental accounting principle that the total value of a company's assets equals the sum of. The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance. The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle. The balance sheet formula is assets = liabilities + shareholders' equity. As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides (or. Assets = liabilities + equity.
The balance sheet is based on the fundamental equation: Assets = liabilities + stockholders’ (or owner’s) equity. As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides (or. Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side. The balance sheet formula is assets = liabilities + shareholders' equity. The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle. Assets = liabilities + equity. The structure of the balance sheet reflects the accounting equation: The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance. The formula reflects the fundamental accounting principle that the total value of a company's assets equals the sum of.
Balance Sheet Represents Accounting Equation Tessshebaylo
The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle. Assets = liabilities + equity. The formula reflects the fundamental accounting principle that the total value of a company's assets equals the sum of. The balance sheet formula is assets = liabilities + shareholders' equity. Assets = liabilities.
Accounting Formula Assets Liabilities Equity Financial Statement
The structure of the balance sheet reflects the accounting equation: The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance. Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side. The balance sheet is based on the fundamental equation: As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides.
Balance Sheet Accounts, Examples, and Equation Financial
As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides (or. Assets = liabilities + equity. The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance. Assets = liabilities + stockholders’ (or owner’s) equity. The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle.
The Balance Sheet Represents Accounting Equation Tessshebaylo
Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side. The formula reflects the fundamental accounting principle that the total value of a company's assets equals the sum of. The balance sheet formula is assets = liabilities + shareholders' equity. Assets = liabilities + equity. The structure of the balance sheet reflects the.
What Is the Accounting Equation? Examples & Balance Sheet
The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle. The balance sheet formula is assets = liabilities + shareholders' equity. Assets = liabilities + stockholders’ (or owner’s) equity. Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side. The structure.
The Accounting Equation A Simple Model
As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides (or. Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side. The formula reflects the fundamental accounting principle that the total value of a company's assets equals the sum of. The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the.
Balance Sheet Meaning, Format & Examples TutorsTips
Assets = liabilities + stockholders’ (or owner’s) equity. The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance. As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides (or. Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side. The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position,.
The Balance Sheet Reflects Accounting Equation Assets Liabilities Owner
As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides (or. The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance. Assets = liabilities + equity. The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle. The structure of the balance sheet reflects the.
The Balance Sheet Represents Accounting Equation Tessshebaylo
The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle. Assets = liabilities + equity. The balance sheet is based on the fundamental equation: As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides (or. The balance sheet formula is assets = liabilities + shareholders' equity.
Balance Sheet Example AccountingCoach
The formula reflects the fundamental accounting principle that the total value of a company's assets equals the sum of. Assets = liabilities + stockholders’ (or owner’s) equity. Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side. The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial.
Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
As such, the balance sheet is divided into two sides (or. Assets = liabilities + stockholders’ (or owner’s) equity. The balance sheet formula is assets = liabilities + shareholders' equity. The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle.
The Accounting Equation Is Also Known As The Basic Accounting Equation Or The Balance.
The balance sheet is based on the fundamental equation: The formula reflects the fundamental accounting principle that the total value of a company's assets equals the sum of. The structure of the balance sheet reflects the accounting equation: Each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry or coverage on the credit side.



/dotdash_Final_Accounting_Equation_Aug_2020-01-5991871f007444398dea7856b442af55.jpg)


/balancesheet.asp-V1-5c897eae46e0fb0001336607.jpg)
