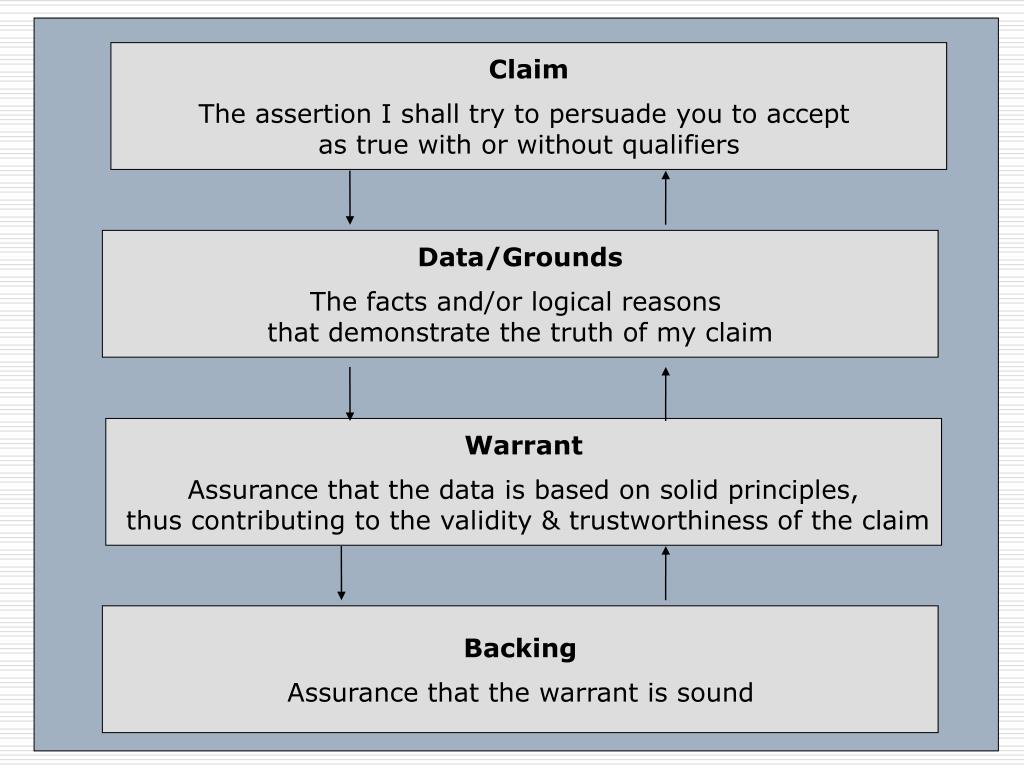
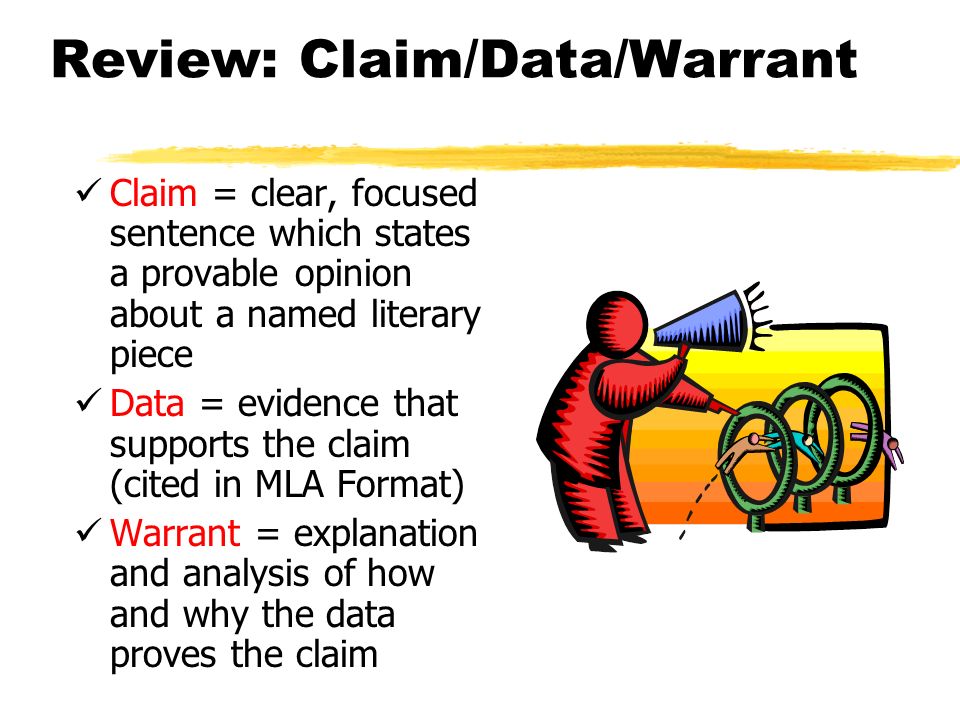
Claim Data Warrant - This resource explains the basic. Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; The warrant, in other words, explains why the data. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. The warrant interprets the data and shows how it supports your claim. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. Learn how to use claim/evidence/warrant (cl/ev/wa) to organize and critique arguments in writing.
The warrant may be explicit or. A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. Learn how to use claim/evidence/warrant (cl/ev/wa) to organize and critique arguments in writing. Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; The warrant interprets the data and shows how it supports your claim. A claim is the assertion that. This resource explains the basic. The warrant, in other words, explains why the data. A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts:
Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason. The warrant interprets the data and shows how it supports your claim. A claim is the assertion that. The warrant may be explicit or. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that. A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. Learn how to use claim/evidence/warrant (cl/ev/wa) to organize and critique arguments in writing. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant.
Toulmin model of argumentation
A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. The warrant may be explicit or. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim;
PPT Analyzing Arguments with Toulmin Model PowerPoint Presentation
A claim is the assertion that. A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: This resource explains the basic. A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant.
PPT CLAIM DATA WARRANT PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The warrant may be explicit or. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. The warrant interprets the data and shows how it supports your claim. A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. The warrant, in other words, explains why the data.
PPT The Toulmin Model of Argument PowerPoint Presentation, free
The warrant may be explicit or. A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that. A claim is the assertion that. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim;
PPT The Toulmin Model PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6134689
The warrant may be explicit or. A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. The warrant interprets the data and shows how it supports your claim. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. This resource explains the basic.
PPT CLAIM DATA WARRANT PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The warrant interprets the data and shows how it supports your claim. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. A claim is the assertion that. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. Learn how to use claim/evidence/warrant (cl/ev/wa) to organize and critique arguments in writing.
PPT CLAIM DATA WARRANT PowerPoint Presentation, free download
In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that. The warrant, in other words, explains why the data. A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. The warrant may be explicit or.
PPT What exactly is “ Claim / Data / Warrant ” ? PowerPoint
The warrant interprets the data and shows how it supports your claim. Learn how to use claim/evidence/warrant (cl/ev/wa) to organize and critique arguments in writing. The warrant may be explicit or. A claim is the assertion that. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;.
PPT CLAIM DATA WARRANT PowerPoint Presentation, free download
A claim is the assertion that. Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason.
What exactly is “Claim / Data / Warrant” ? ppt video online download
A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. The warrant, in other words, explains why the data. A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that. A claim is the assertion that. This resource explains the basic.
The Data (Also Called Grounds Or Evidence ), Which Support The Claim;.
The warrant interprets the data and shows how it supports your claim. A claim is the assertion that. Learn how to use claim/evidence/warrant (cl/ev/wa) to organize and critique arguments in writing. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant.
Toulmin Identifies The Three Essential Parts Of Any Argument As The Claim;
In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason. A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that.
The Warrant May Be Explicit Or.
The warrant, in other words, explains why the data. This resource explains the basic.