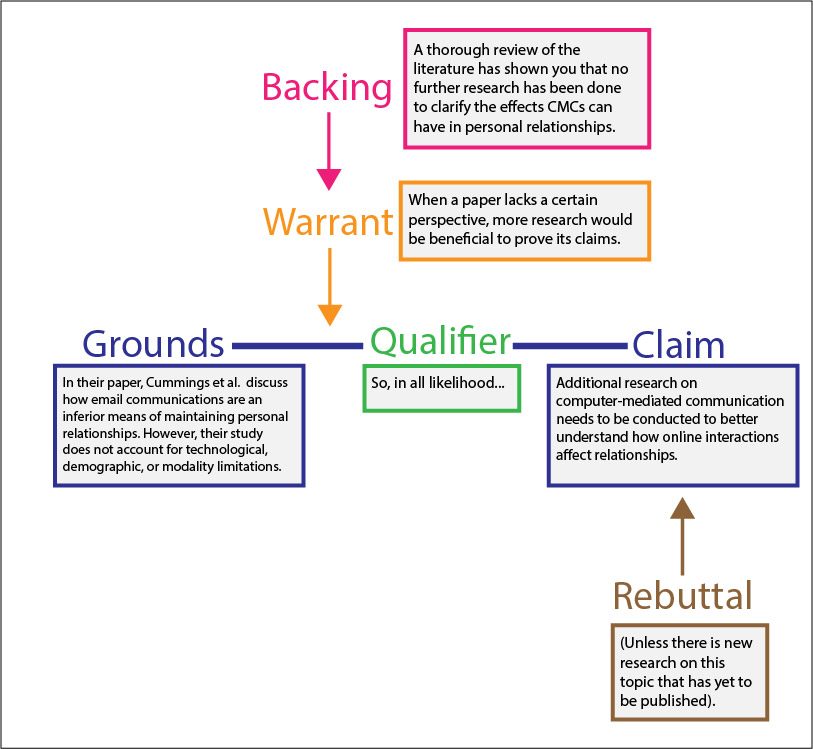
What Is A Warrant In An Argument - What is a warrant in argumentative writing? Learn when and how to use warrants, and see an example. Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. A claim is the assertion that. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: In many arguments, warrants are often. A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in.
What is a warrant in argumentative writing? Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in. In many arguments, warrants are often. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: Learn when and how to use warrants, and see an example. Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. A claim is the assertion that. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant.
Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. A claim is the assertion that. What is a warrant in argumentative writing? Learn when and how to use warrants, and see an example. In many arguments, warrants are often. A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in. Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts:
Toulmin’s Argument Model ppt download
What is a warrant in argumentative writing? Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: Learn when and how to use warrants, and see an example. In many arguments, warrants are often.
The Toulmin Model of Argument ppt download
A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. What is a warrant in argumentative writing? Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with.
PPT The Logical Structure of Arguments PowerPoint Presentation, free
A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in. What is a warrant in argumentative writing? A claim is the assertion that. Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts:
PPT Writing Module Three Five Essential Parts of Argument PowerPoint
Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. What is a warrant in argumentative writing? In many arguments, warrants are often. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener.
Introducing the Toulmin Model YouTube
In many arguments, warrants are often. What is a warrant in argumentative writing? Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in.
PPT Argument terms PowerPoint Presentation ID2095605
A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. What is a warrant in argumentative writing? Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. A claim is the assertion that.
PPT Argumentative Writing Based upon the Stephen Toulmin Model For
The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. A claim is the assertion that. Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts:
Read The Claim. Then Explain The Warrant
A claim is the assertion that. Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in. Learn when and how to use warrants, and see an example. In many arguments, warrants are often.
Toulmin's Argument Model
Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. In many arguments, warrants are often. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument.
PPT Toulmin’s Model of Argumentation PowerPoint Presentation ID1102469
A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: In many arguments, warrants are often. Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be.
The Claim, The Grounds, And The Warrant.
Learn when and how to use warrants, and see an example. Warrants are underlying beliefs that connect reasons and claims in an argument. A claim is the assertion that. In many arguments, warrants are often.
In Toulmin’s Method, Every Argument Begins With Three Fundamental Parts:
Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. What is a warrant in argumentative writing? A warrant is a underlying assumption or principle that connects the claim to the data in.