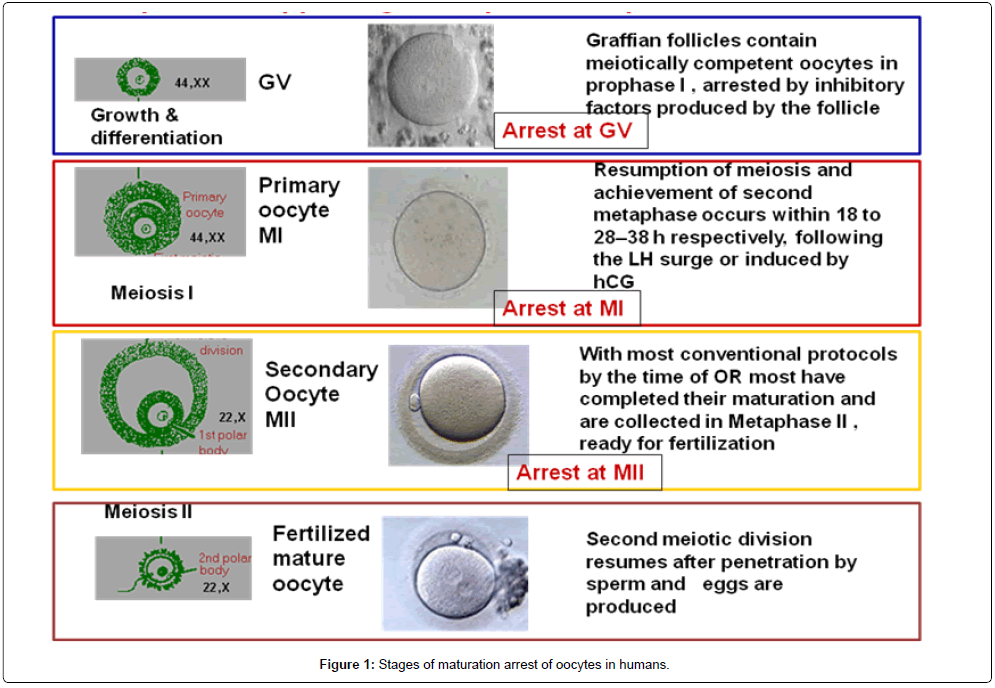
When Are Oocytes Arrested - This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c. This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest as well as the signaling. The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of the second meiotic division. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an interphase microtubule. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation.
Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest as well as the signaling. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c. Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an interphase microtubule. The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of the second meiotic division.
Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an interphase microtubule. The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of the second meiotic division. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest as well as the signaling. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c.
Stops and starts in mammalian oocytes recent advances in understanding
The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of the second meiotic division. Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an interphase microtubule. This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. Oocytes are held in.
Setdb1 KO oocytes show severe meiotic arrest. (A, B) Oocytes harvested
This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest as well as the signaling. The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of the second meiotic division. This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh).
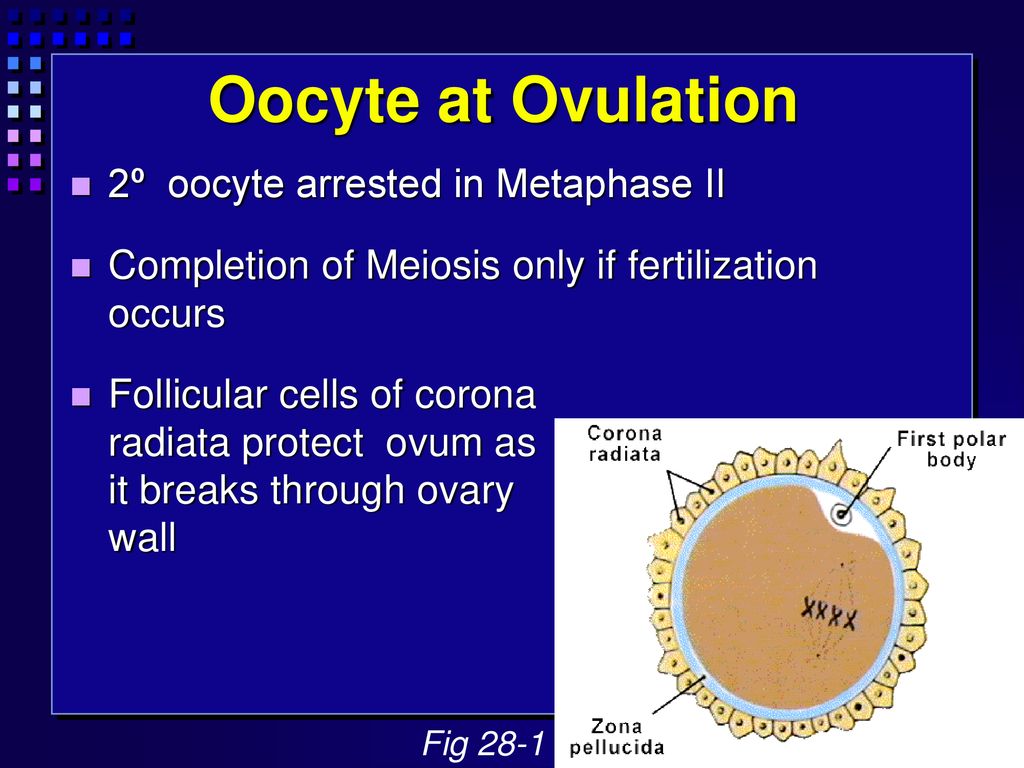
Ch28 Human Development Explain the stages of development starting with
Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an interphase microtubule. This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest.
Activation of APC/C in metaphase IIarrested oocytes containing or
The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of the second meiotic division. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an interphase microtubule. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. This review addresses.
DNA damage models and impact of DNA damage on oocytes. (A) Oocyte
This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest as well as the signaling. The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of the second meiotic division. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. This metaphase block is caused by the.
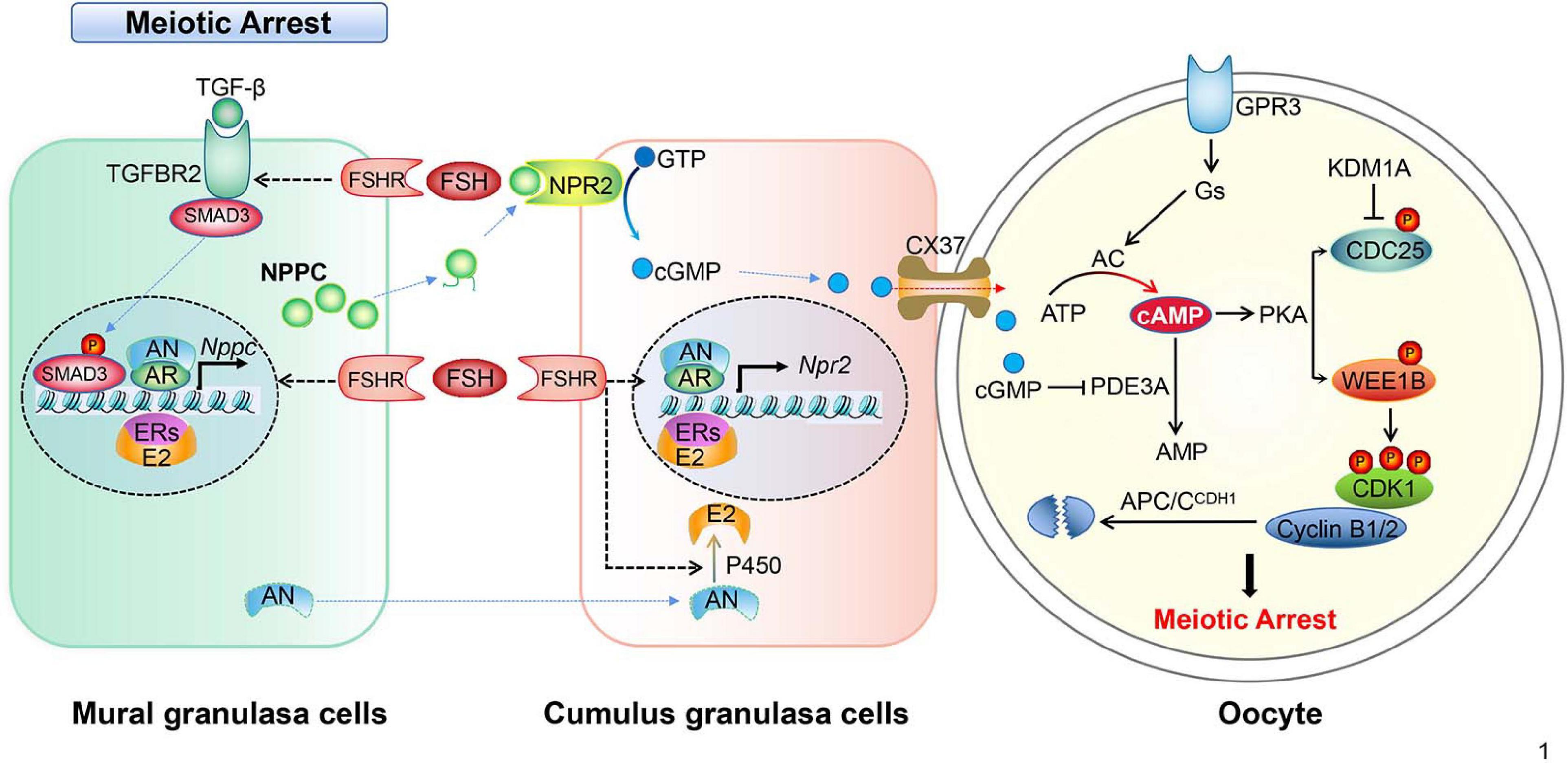
Meiotic Arrest
The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c. This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest as well as the signaling. The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of.
The DNA damage checkpoints in mammalian oocytes. DSBs that lead to
Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an interphase microtubule. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c. This review addresses the underlying.
Meiotic Arrest
This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest as well as the signaling. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an interphase microtubule. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i.
Is age‐related increase of chromosome segregation errors in mammalian
The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of the second meiotic division. This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c. Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized.
metabolomicsoocyteshumans
This metaphase block is caused by the combined actions of c. This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest as well as the signaling. The ovulatory luteinizing hormone (lh) surge promotes the resumption. Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an.
This Metaphase Block Is Caused By The Combined Actions Of C.
Oocytes are found in the ovary, are arrested in prophase of meiosis i, are characterized by an intact nucleus, have an interphase microtubule. The oocyte is arrested again in the metaphase of the second meiotic division. Oocytes are held in meiotic arrest in prophase i prior to ovulation. This review addresses the underlying mechanisms involved in maintaining the oocyte in meiotic arrest as well as the signaling.